What Does 40 To 1 Odds Mean
- What Does 40 To 1 Odds Mean Football
- What Does 5 To 1 Odds Mean
- What Does 40 To 1 Odds Mean For A
- What Does +100 Odds Mean
For example, if the odds are +750, the bettor would receive $750 dollars if their bet was successful. If the odds were -750, the bettor would have to wager $750 in order to profit $100 (and therefore receive back $850 in total). Now you can tell that $7.50, 13/2 and +650 all mean the same thing and the need for an odds.
The odds converter tool in this page will convert odds from any of the three main formats into the other formats.
It will also calculate the relevant implied probability too.
To use it, simply enter the odds you wish to convert in the appropriate box, and then click the “Convert Odds” button. It’s as easy as that!
- Fractional odds are some of the most simple to understand, as they present your potential winnings as a fraction of the money you stake: while the denominator represents the amount bet, the numerator is the amount your stake will yield in a winning bet. For example, odds of 1/1 mean you’d get a return of $20 for a winning $10 bet.
- 40/1 is an exceptional return on a bet and if it comes in, you’re laughing. A horse with odds of 40/1 would be classed as an ‘Outsider’ or ‘Longshot’ and if the race has only a few runners then it’s statistically unlikely that you will win.
What Does 40 To 1 Odds Mean Football
If you came to this page specifically looking for a tool to
convert odds, then it’s likely that you already have a
fundamental understanding of what odds are and how they work in
relation to sports betting. If this is a subject that you’re not
particularly familiar with, however, then you might want to read
the following article from our beginner’s guide to sports
betting.
Odds Conversion Math
Overview of Different Odds Formats
If you live in the United States, then simply knowing the
moneyline odds will suffice, as this is the primary format used
by the limited number of gambling sites available for US
residents. Likewise, if you live in the United Kingdom, then you
only really need to know how fractional odds work. If you live
in Europe, then the decimal format is the one that will be most
important for you to understand.
With all that being said, it’s still a good idea to be
familiarized with how each format works. Many online betting
sites will allow you to choose the format that their odds are
displayed in. Please keep in mind that the conversation may
round in their favor.. For example, most US friendly sites offer
moneyline odds of -110 when betting points spreads. If you
choose to bet in the decimal format instead, then you’ll often
be given odds of 1.90. The true conversion is 1.9091 though, so
you’ll potentially lose a small percentage of your winnings if
you bet based on their conversion.
Therefore, it can be an advantage to use the primary format
offered by an online bookmaker, which is why it pays to make
sure you understand each of the different formats. We’ve
explained them all below for you.
American Odds/Moneyline Odds
Odds in this format are expressed as either a positive number
or a negative number. When they are a positive number, the
number represents how much in winnings is paid per $100 staked.
The following examples illustrate how positive moneyline odds
work.
When they are a negative number, the number represents the
amount of money that needs to be staked in order to win $100.
The following examples illustrate how negative moneyline odds
work.
Please see our article on calculating payouts from moneyline
odds for details on how to work out the potential winnings from
wagers using this format.
Decimal Odds
This is the most popular odds format outside of the United
States and is sometimes referred to as European odds. It’s a
very simple format where the odds are expressed as a single
positive number, usually to two decimal places. This number
states how much a winning bet returns (including the initial
stake) for each unit wagered. The following examples illustrate
the decimal format in practice.
Our article explaining how to calculate payouts from decimal
odds will teach you how to work out the potential returns from
wagers placed using this format.
Fractional Odds
Fractional odds are mostly used in the UK, but lately the
decimal format has been becoming more popular. Odds in this
format are displayed as a fraction, as the name suggests. The
first number of the fraction shows how much you can win per the
second number staked. This sounds more complicated that it
actually is and the easiest way to understand this format is
simply to look at some examples.
Please note that when the second number of the fraction is
higher than the first, it means the odds are less than even
money. This is referred to as odds on (as opposed to odds
against), and is the equivalent of when moneyline odds are a
negative number or when decimal odds are a number less than 2.
Odds Conversion Math
Our conversion tool is the easiest way to change odds between
formats but there will be times when you don’t have access to
it. When you’re at a Las Vegas sportsbook or a high street
bookmaker, you may need to be able to do these conversions in
your head. For this reason, we’ll run through the math required
to convert each format into all of the other formats.
Converting Moneyline Odds
To Decimal
The calculations required to convert from moneyline odds
changes depending on whether the odds are positive or negative.
To convert positive odds into decimal odds, the following
calculation is required.
Example: Converting +175
(+175 + 100) / 100 = 2.75
For negative odds, we ignore the minus symbol and use the
following formula.
Example: Converting -110
(110 + 100) / 110 = 1.909
To Fractional
When converting from the moneyline format into the fractional
format, the calculations again depend on whether the odds are
positive or negative. To convert positive odds, you simply
create a fraction by putting the relevant number over 100 and
then simplifying the fraction if possible.


300/100 is simplified to 3/1
To convert negative odds, you create a fraction by putting
100 over the relevant number (ignoring the negative sign).
Again, you then need to simplify the fraction if possible.
100/110 is simplified to 10/11
Converting Decimal Odds
To Moneyline
The method required to convert the decimal format over to the
moneyline format is dependent on whether the odds are greater
than 2.0 or not. We’ll look at how to convert odds of 2.0 or
less first. To start with, you have to carry out the following
calculation.
After doing this calculation, the odds are rounded and a
negative sign must be added.
100 / (1.95 – 1) = 105.25
To convert odds of greater than 2.00, you must start with the
following calculation.
To convert odds of greater than 2.00, you must start with the following calculation.
You then add a positive sign to the result, as shown in this
example.
(2.45 – 1) x 100 = 145
Positive sign added = +145
To Fractional
The first step in converting from decimal to fractional
format is to create a fraction by using the formula.
This will often create a fraction that includes a decimal,
which isn’t a proper fraction. To overcome this, the next step
is to multiply both sides of the fraction by 100. Finally, the
fraction needs to be simplified. The following example
illustrates this better than any written explanation can.
(1.45 – 1) / 1 = 0.45/1
Multiply both sides by 100 = 45/100
Simplified = 9/20
What Does 5 To 1 Odds Mean
Converting Fractional Odds
Before we get into the math involved here, you need to
understand the terms numerator and denominator. In this context,
the numerator is the first number in the fraction and the
denominator is the second number in the fraction. With odds of
2/1, for example, 2 is the numerator and 1 is the denominator.
To Moneyline
There are two methods needed for converting from the
fractional to the moneyline format. The first is for when the
numerator is greater than the denominator. The following formula
needs to be used in the beginning.
A positive sign then needs to be added to create the
moneyline odds, as per the following example.
(6 / 4) x 100 = 150
Positive sign added = +150
The second method is for when the denominator is larger than
the numerator. In these cases, the following formula needs to be
used.
A positive sign then needs to be added to create the correct
moneyline odds. This is illustrated in the following example.
100 / (2 / 5) = 250
Negative sign added = -250
To Decimal
Converting odds from the fractional format to the decimal
format is relatively simple and it requires just the following
formula.

What Does 40 To 1 Odds Mean For A
(11 / 10) + 1 = 1.10
What Does +100 Odds Mean
Implied Probability Explained
Implied probability in relation to sports betting is
basically the implication of the odds as it relates to the
chances of an outcome happening. We’ll cover this in more detail
shortly, but first let’s look at how to calculate it. It’s
easiest to determine implied probability from odds in the
decimal format, using the following simple formula.
What this example shows us is that the implied probability of
2.50 odds is 0.40 (or 40% if expressed as a percentage). This
means that odds of 2.50 on any possible outcome imply that the
chance of that outcome happening is roughly 40%. So if, for
example, a tennis player is at 2.50 to win an upcoming match,
the implication is that he has a 40% chance of actually winning
that match.
You can read more about implied probability in this article on probability in sports betting. The article also
covers expected value, which is a related topic that you should definitely learn about if you want to be a
successful bettor.
Understanding Vig
When looking at the odds set by bookmakers, it’s important to
recognize that implied probability is rarely an entirely
accurate reflection of the real chances of a wager winning. This
is because bookmakers always try to set the odds at levels that
are lower than they actually should be in relation to real
probability. If their view was that a soccer team had a 60%
chance of winning a match, for example, they wouldn’t offer odds
that exactly reflected that chance. Their odds would be lower,
as this is how they make money successfully.
By reducing the odds relative to the probability of an
outcome happening, bookmakers effectively charge a commission
for every wager they take. This commission is known as vig,
which is short for vigorish. It can also be referred to as the
overround or juice. It’s similar in some respects to the house
edge in casino games and it’s basically what gives the
bookmakers an advantage over their customers.
What sets the bookmakers’ advantage apart from the casinos’
advantage is that, unlike the house edge, it can be overcome. In
order to overcome it, though, you first need to understand
exactly how vig works and the effect it has in sports betting.
You should visit our page on the subject of how bookmakers make
money, as this is all about the methods that bookmakers use to
ensure they are profitable. Charging vig is one of these methods
that we explain thoroughly.
If you want to come out on top against the bookies it is vital that you understand the fundamentals. When it comes to sports betting there is nothing quite as fundamental as the odds that the bookies offer. Unfortunately, betting odds can prove very confusing. That’s especially true for people who are new to betting.
That’s where this article comes in. We’re going to explain exactly how betting odds work, how they are set and the differences in the ways they are displayed. After taking in all the information below, you will be much better equipped to set about making some profit.
What Do Betting Odds Represent?
At their most basic, betting odds tell you two things:
- How much you stand to make should the selection win
- The probability of the selection winning
Take this example. If you were looking through the weekend Premier League fixtures and saw a team had fractional odds of 2/1 (that’s decimal odds of 3.0) you would know that you stand to win £2 in profit from every £1 that you stake should the team win. You’d also know that the bookmaker who set the odds ranks the team’s chances of winning as one in every three times the game is played.
If you saw a team had fractional odds of 8/13, you’d know that for every £13 you stake, you will win £8 or profit and that if the game was played 21 times in total, the bookies think the team would win 13 times and fail to win eight times (what is known as the implied probability).
Working out an implied probability percentage from fractional odds is simple. You just divide the stake by the combined sum of the two numbers which make up the fractional odds. In the case of 2/1 the equation looks like this:
1 / (2+1) = 0.33 or 33%
For odds of 8/13 this is the equation:
13 / (8+13) = 0.62 or 62%
That’s how the maths works but when it comes to the actual odds that bookmakers set, it’s a little more complicated.
How Do Bookmakers Set Their Odds?
The basic business model of a sportsbook is fairly uncomplicated. Bookmakers set the odds and take bets on an event. When that event ends they pay out everyone who backed the winner and then keep the rest for themselves.
But, consider the following horse race.
| Selection | Fractional Odds | Decimal Odds | Implied Probability | Profit From a £10 Bet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horse 1 | Evens | 2.0 | 50% | £10 |
| Horse 2 | 3/1 | 4.0 | 25% | £30 |
| Horse 3 | 7/1 | 8.0 | 12.5% | £70 |
| Horse 4 | 7/1 | 8.0 | 12.5% | £70 |
As you can see, the combined implied probability of the selections above is 100%. From a bookmaker’s perspective that is a big problem. That’s because, presuming they’ve got the same amount of liability on each selection, they’d never make any money as they’d have to collect and payout the same amount.
So, the bookmakers will build something called an overround into their odds. Here’s a real example of a match odds market from a football match:
| Selection | Fractional Odds | Decimal Odds | Implied Probability | Profit From a £10 Bet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Man Utd | 1/2 | 1.5 | 66.7% | £5 |
| Draw | 18/5 | 4.6 | 21.7% | £36 |
| West Ham | 13/2 | 7.5 | 13.3% | £65 |
With an total implied probability of 101.7%, the bookmaker who set those odds is guaranteed to make a profit of 1.7% assuming that they have the same amount of liability on all three selections. Of course, it rarely works out that the bookies manage to spread their liability evenly but you need to know that when you look at a betting market you’re not simply looking at a reflection of how the bookies think the event will pan out. There’s much more going on behind the scenes.
Armed with this knowledge of how the bookmakers set their odds, you can concentrate on finding value. That is, finding a bet where you believe the odds (and therefore the implied probability) is too big. If the bookies think that a side has a 50% chance of winning but you think they’ve got a better chance than that, that’s value.
The Difference Between Decimal and Fractional Odds
You will have seen above that we’ve spoken about both fractional and decimal odds. They are just different ways of conveying the same information but they do add another layer of complexity.
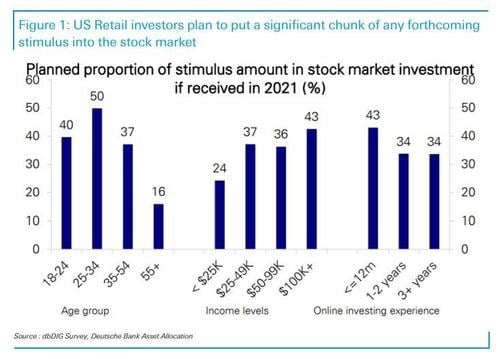
All the major online bookmakers will shows their odds as both fractions and decimals so it’s important that you understand just what they are showing and how to switch between the two. Thankfully, it only requires simple maths.
To go from a fraction to a decimal is as easy as dividing out the fraction and adding one. Here’s how that looks for odds of 2/1:
(2/1) + 1 = 3.o
And using our second example from above, 8/13, it looks like this:
(8/13) + 1 = 1.62
If you want to go from decimal odds to fractional odds is similarly simple. You just minus one from the decimal odds, turn that number into a fraction and reduce it down to it’s simplest form.
Let’s take decimal odds of 4.5, this is the equation:
4.5 – 1 = 3.5
35/10 -> 7/2
If the decimal price is 1.25, you convert it into fractional odds like this:
1.25 – 1 = 0.25
25/100 -> 1/4
Here’s a list of some of the most common fractional odds and their decimal equivalents (for a more in-depth list click here).
| Fractional Odds | Decimal Odds | Implied Probability |
|---|---|---|
| 1/10 | 1.10 | 90.9% |
| 1/5 | 1.2 | 83.33% |
| 2/5 | 1.4 | 71.43% |
| 1/2 | 1.5 | 66.67% |
| 1/1 (evens) | 2.0 | 50% |
| 3/2 | 2.5 | 40% |
| 2/1 | 3.0 | 33.33% |
| 4/1 | 5.0 | 20% |
| 9/1 | 10.0 | 10% |
| 100/1 | 101.0 | 0.99% |
Key Terminology
When reading betting advice or searching for a value bet on the bookies’ websites you’ll come across some key terms relating to betting odds. To round up our article on betting odds, we’ve covered the most widely used terms to ensure you don’t get confused in your search for winners.
Stake – The amount of money that you place (or wager) on a specific bet.
Price – The price of a bet is simply another way of referring to the odds. You can either say that a football team can be backed at odds of 2/1or that their price is 2/1.
Odds On & Odds Against – Two of the key terms that you’ll hear when it comes to betting odds are ‘odds on’ and ‘odds against’. These terms refer to whether a price is greater or lower than evens. Any price above evens is known as odds against, while anything below evens is odds on.
Short and Long Odds – If something is described as being short odds it means the price is low. A long odds shot will provide you with a bigger win but is much less likely to win.